(1) Method characteristics
The shallow hole mining ore mining method is characterized by dividing the stage into ore blocks, and the ore blocks are further divided into mining houses and pillars for secondary recovery. The mining room is layered and stratified from top to bottom, and each time the ore that has collapsed is released about one-half, and the rest is stored in the mine room as a workbench to continue mining. After the mining room is finished, it is released, and the mining room is finished. Back to the mining column and processing the gob.
(2) Applicable conditions
The shallow hole ore mining method is mainly used to open ore and stabilized ore bodies. It is generally suitable for medium-thick, thin or still thin ore bodies. The ore body inclination angle is generally required to be not less than 60° in thin veins. Generally, the body is required to be not less than 55°. The smaller the dip angle, the more difficult it is to mine, and the greater the workload of powder mine loss and flat field. Because of the large amount of ore stored in the mine, the ore and surrounding rock cannot be self-igniting, oxidizing and agglomerating.
c) Components
When the thickness of the ore body is less than 15m, the ore blocks are arranged along the strike. When the thickness of the ore body is greater than 15m, the ore blocks are arranged vertically. Divide the nuggets into mines and pillars, and then mine the post-mining pillars. The length of the nugget is 40 to 50 m and the height is 40 to 50 m. The height of the top column is 4m, the height of the bottom column is 6m, the width of the column is 6m, and the spacing between the links is 5.5-6.0m.
(4) Precision cutting
The mining and cutting work mainly includes excavating the middle section of the transportation lane, the patio and the patio connecting road. The bottom pillar is digged into the bottom of the bottom and the funnel neck is digged every 5~7m, and the bottom is cut and the leakage is formed to form the mining free surface.
For the cutting work, the 7565 type pneumatic leg rock drill is used for the roadway excavation, and the YSP45 rock drill is used for the tunnel excavation. The mining roadway is generally unsupported, the local unstable section adopts wooden support, and the extremely unstable zone adopts concrete reinforcement support.
(5) Mining work
1. Mining sequence: The mining work mainly includes rock drilling, blasting, ventilation, partial ore mining, dome flat field, and large amount of mining. Since the mining work is carried out from the bottom level from the bottom to the top, the layer height is generally 2.0 to 2.5 m. In the stope, the 7655-type gas-leg rock drill is used to drill the upward micro-fronting blasting hole. The drilling blasting parameters are: the minimum resistance line is 1.0-1.2m, the blast hole spacing is 0.8-1.0m, and the hole depth is 1.8-2.2m. The front and rear rows of blastholes are staggered, using ammonium nitrate explosives for manual charging, and millisecond non-conducting squibs for detonation. The fresh air flow enters the stop working face from the middle section of the transport roadway through the patio and patio contact road on the side of the mine. The dirty wind passes through the patio contact road on the other side of the mine house and the patio enters the upper middle section transport (return air) roadway. The ore that has collapsed in the stopway relies on gravity to release about one-third of the ore deposit, and then performs the dome, flat field and secondary blasting work. After the recovery of the mining house, a large amount of ore mining work is organized to release all the ore remaining in the mine. The ore is loaded into the mine car through the funnel and discharged through the middle section of the roadway.
2. Rock blasting: The rock in the stope is drilled with a 7655 air leg rock drill. The hole spacing and row spacing are 0.6-0.8m, the hole depth is 2.1m, and the blastholes are staggered. Manually installed No. 2 rock explosives, detonators and non-conducting blasters detonated.
3. Mining and mining: The ore is loaded into the mine by self-weighted manual gates for recovery and mining.
(6) Mining and mining of mined pillars
The pillars are harvested by the caving method. In order to ensure the safety of the mining work of the pillars, before the large amount of ore mining in the mine, the blastholes in the mine room column and the top of the roof are drilled, and all the ore in the mine room is released, and then the column is blasted. Generally, the column is first exploded, and the top and bottom columns are post-explosive.
At the same time as the pillars are harvested, the goaf should be treated in a planned manner by natural or forced collapse of surrounding rock.
(7) Ventilation and dust prevention in the stope
The fresh air flow enters the stop working face from the main ascending well, the stage transporting alley, the side patio and the patio contact road, and the dirty wind passes through the other side patio connecting road, the patio, the return airway road to the return air well. Ventilation in the stope should be supplemented by a local fan.
Wet rock drilling and dust collection in the pit; when the single head working face is excavated, the fan is used to ventilate the dust; when the rock mine is installed, the dust is sprayed on the explosion pile; the sluice gate and the unloading port are installed with a sprayer to reduce the dust; Wall treatment; underground workers wear dust masks.
(8) Mining loss rate and depletion rate
According to the selected shallow hole mining method, combined with the actual situation of small ore bodies in Baotou area, the ore recovery rate is generally about 92%, and the loss rate is about 8%.
Second, the application of shallow hole mining and mining method
(A) small iron ore mine types and morphological occurrence Baotou
The natural type of ore in small iron ore deposits in Baotou area is generally quartz -type magnetite ore, and most of the industrial types are weakly magnetic and iron ore is selected. Most of the ore deposits have ω(mFe)/ω(TFe) between 15% and 85%, which is mixed ore. The genetic type of the deposit is basically the metamorphic ferrosilicon of the sedimentary metamorphic iron deposit to form iron ore.
The ore body generally exists in the hornblende slant gneiss , and the output is controlled by the stratum, which is layered, layered, lenticular, and the like. Most of the ore bodies are steeply inclined ore bodies, and the inclination angle is generally 60 to 85°. The thickness of the ore body is medium or very thin ore body, generally 3 to 20 m, mostly around 10 m.
(II) Surrounding rock conditions of the ore body
The surrounding rock of the ore body is mainly mixed igneous hornblende gneiss and black cloud hornblende gneiss. There are generally less stones in the ore body. The boundary between the ore body and the surrounding rock and mezzanine is clear.
(3) Hydrogeological conditions
The aquifers in each mining area of ​​Baotou area are mainly the Quaternary alluvial aquifer and the weak aquifer of the bedrock fissure. The lithology of the Quaternary alluvial aquifer is a gravel layer, and the amount of water inflow is generally small (except for the Laigou iron ore). The lithology of the weak aquifer in the bedrock fissure diving is mostly slanted long-horned flash gneiss, granite , quartz diorite, etc. The weathering fissure is relatively developed, and the water permeability is good, but the water-rich is weak. The topographic conditions of most mining areas are conducive to drainage, and the groundwater ditch directly receives vertical infiltration replenishment of atmospheric precipitation. In short, the small iron ore deposits in Baotou area are mainly filled with fissure water, the second is the void water, the water content is weak, the recharge conditions are poor, the natural drainage conditions are good, and the hydrogeological exploration type of the deposit is the second type first type, ie hydrology. The geological conditions are simple.
(4) Engineering geological conditions
Most of the fault structures in the mining area are extremely undeveloped. The surrounding rock of the top and bottom of the ore body is a semi-hard-hard layered rock stratum. The tensile, compressive and shear strengths are large, and the overall rock stability is strong. There is basically no bad engineering geology. problem. The geological type of deposit exploration engineering belongs to the second type, the first type, which is a mining area with simple engineering geological conditions dominated by hard rock layers. However, the long-term exposure of the rock mass is subject to weathering, and the surface weathering fissure is relatively developed, which causes the integrity of the rock mass to be destroyed, the mechanical strength is reduced, the stability is weakened, and the sliding is easy to occur, which is the main unfavorable factor for the mining.
(5) Environmental geological conditions
According to Figure A1 of "China Earthquake Peak Acceleration Zoning Map" (GB18306-2001), the peak acceleration of Baotou area is 0.15~0.30g, and the contrast intensity is 7.5~8.5 degrees, all of which are seismic fortification areas.
The ecological environment in Baotou is relatively fragile, and mining will change the natural topography of the area, destroying the recharge route and permeability of groundwater. Due to the lack of vegetation in most mining areas, the relative height difference of the topography is large, and the waste rock discharged from the mining is easy to form a small-scale debris flow during rainfall. Therefore, in the mining process, we must pay attention to the unified management and treatment of waste rock, waste residue and wastewater, strengthen the construction and protection of the ecological environment, and avoid pollution and damage to the environment as much as possible.
The stratigraphic lithology of Baotou area is mainly composed of some low gamma value gneiss and magnetite quartzite . The variation of gamma value is relatively stable, and it is the area with low radioactive bottom value.
(6) Adaptability
According to the applicable conditions of the shallow hole mining method, combined with the scale, shape, occurrence and hydrological, engineering and environmental geological conditions of small mines in Baotou, this method is very suitable for most small mines. The mining method is simple in process, easy to grasp, and has good safety. It is recommended to promote the use of mines.
(7) Current status of application
Baotou past two years, many small mines using a shallow hole in the production process shrinkage stoping method, there is a good application Guyang hole No. 1 iron ore silver white, No. 7 iron ore, iron ore No. 12, No. 29 Iron ore, Baotou Steel Guyang Mining Company Public Welfare Mingtie Mine, Guyang County Liuding Account Iron Mine, etc., the annual production scale of these mines is about 150,000 tons.
(8) Problems and suggestions
1. Although many small mines adopt the shallow hole mining and mining method, there are some roads mining methods that are suitable for adopting this method, but adopt the roadway mining method with poor safety, large amount of mining and cutting, and low ore recovery rate. It is recommended that these mines modify the mining method after examining the mines where the method is applied well.
2. In mines where this method has been applied, some applications are not standardized or unscientific and should be improved. For example, some mines are thicker and reach 20m. When the method is applied, no ore outlets are set up in the upper and lower plates of the ore body. The ore in the mine is not clean, resulting in waste of resources. Some mines did not return to the mining column in time after the end of ore mining in the mine, which also resulted in low resource recovery rate.
3. It is necessary to deal with the gobs in time. Most of the mines in the Baotou area that applied the shallow hole mining and mining method did not deal with the goaf in time after the completion of a middle section, resulting in a large safety hazard. It is recommended that the mine should return to the mining column in time and collapse the surrounding rock to treat the goaf. After the collapse of the surrounding rock, the mine should set up fences around the subsidence area in time to prevent people, animals and vehicles from entering the city and causing safety accidents.

Aluminum Printed Circuit Board, Recognized Best Solutions for High Power and High Thermal Conductivity
As for aluminum PCB, we will elaborate on the following aspects
- What is Aluminum PCB?
- More Detailed Introduction of Aluminium PCB
- Aluminum PCB Structure
- Aluminum PCB Advantages
- Aluminum PCB Applications
- Types of Aluminum PCB
- Aluminum PCB Performance
- Classification of Aluminum PCB
- Manufacturing Difficulties of Aluminum PCB
- Design Guidelines For Aluminum PCB
As a Chinese PCB manufacturer, Jinghongyi PCB has rich experience in manufacturing aluminium PCB board. It provides customers with high-quality aluminium PCB manufacturing and one-stop aluminium PCB turnkey assembly services, prompt delivery on time, and competitive prices.
What is Aluminum PCB
Among all metal core PCBs, aluminum core PCB is the most common type, also known as IMS (Isolated Metal Substrate). Due to its low cost, non-toxic and environmental protection, higher durability and lightweight characteristics, aluminum clad PCB is widely used, and its main task is to dissipate the heat generated by power components. For example, it is used in high-power LED lighting power supply, power module, automobile power controller, computer CPU motherboard, etc.
According to the different design structure and application scenarios of aluminium PCB, there are mainly Flexible aluminium PCB, mixed aluminium PCB, multi-layer aluminium PCB, through-hole aluminium PCB and so on.
More Detailed Introduction of Aluminium PCB
Using heat-sinks increases the costs and makes assembly more difficult, and the extra weight and volume can cause problems.Safe and effective heat dissipation is very important in applications where high power components generate a lot of heat. Although forced cooling is a method, the disadvantage of forced cooling is that it produces disturbing noise, vibration and increased energy consumption while refrigerating. The use of additional radiators increases costs and makes assembly more difficult, and additional weight and volume can cause other unnecessary problems.

Using a specific PCB structure is usually a better solution. The commonly used solution is the metal core structure. With this solution, the printed circuit board is composed of aluminum plates bearing track patterns. Thermoelectric insulators are used between the track and the board so that heat can pass through the metal core structure, such as the Metal Core PCB.
While LED lighting is widely used, it is also necessary to eliminate the heat generated by LED lighting. Therefore, the development of LED lighting industry directly leads to the increase of PCB using aluminium core. At the same time, the market demand of LED PCB board is also growing.
Copper may be used as an alternative.
For high-power LED, most customers use aluminum-based PCB; for low-power LED, standard Fr4 PCB is also available. Our PCB manufacturing specifications and construction of most types of metal-based printed circuit boards.
Aluminum Based PCBs are a unique metal-based copper clad laminate. These types of Printed Circuit Boards have good thermal conductivity, electrical insulation and very solid machining performance.
They are also known as Aluminum Clad, Aluminum base, MCPCB (Metal Clad Printed Circuit Board), IMS (Insulated Metal Substrate), Thermally Conductive PCBs etc. Aluminum PCBs were developed in the 1970s, soon after which they`re applications increased dramatically. The first application was their use in Amplification Hybrid Integrated Circuits. Now they are being used at a large scale due to which it is necessary for us to have an idea of Aluminum PCBs and their importance.
Aluminum PCB Structure
AluminumPCBs are actually quite similar to FR4 PCBs. The basic structure of Aluminum PCBs is four layered. It consists of a layer of copper foil, a dielectric layer, an aluminum base layer and aluminum base membrane.
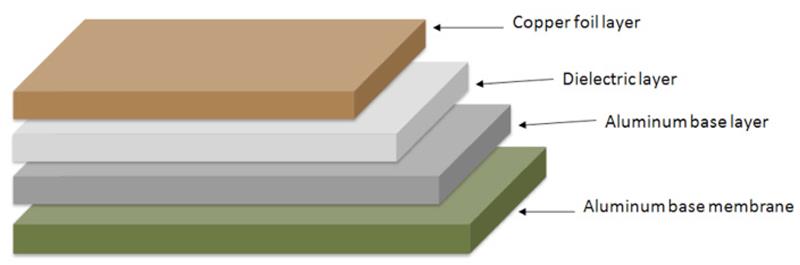
- Copper Foil Layer: the copper layer used is relatively thicker than normal CCLs ( 1oz-10oz). A thicker layer of copper means a larger current carrying capacity.
- Dielectric Layer: the Dielectric layer is a thermally conductive layer and is around 50μm to 200μm thick. It had a low thermal resistance and it suitable for its application.
- Aluminum Base: The third layer isthe aluminum base which is made up of aluminum substrate. It has a high thermal conductivity.
- Aluminum Base Membrane Layer: Aluminum base membrane is selective. It has a protective role by keeping the aluminum surface safe from scraping and unwanted etching. It is of two types i.e. Lower than 120 degree or around 250 degrees (anti high temperature)
Aluminum PCB Advantages
- Lower manufacturing and use costs: Aluminum is a metal that can be found in a variety of climates, so it is easy to mine and refine. Therefore, the costs of doing so are significantly lower than other metals. In turn, this means that manufacturing products with these metals are less expensive as well.Aluminum is a very common metal raw material, its mining and production are very convenient. Therefore, the cost of doing so is significantly lower than that of other metals. Conversely, this means that products made from these metals are also cheaper.
- More energy-saving and environmentally friendly: Aluminum is non-toxic and recyclable. Because it is easy to assemble, the use of aluminium also helps to save energy. For PCB vendors, the use of this metal helps to maintain the health of our planet.
- Better heat dissipation performance:Efficient heat dissipation is the greatest advantage of aluminium PCB. High temperature can cause serious damage to electronic equipment, so it is wise to use materials that can help heat dissipation. Aluminum can actually transfer heat from important components to minimize its harmful effects on circuit boards.
- Higher strength and durability: Aluminum provides strength and durability to a product that ceramic or fiberglass bases cannot. Aluminum is a sturdy base material that can reduce accidental breakage during manufacturing, handling, and everyday use.
- Lighter weight and better elasticity: Aluminum is widely recognized as a light metal. While increasing the heat dissipation performance of high power components, it also reduces the weight of the product itself, and increases the strength and elasticity. In addition, in the transportation of products, lighter weight also saves the transportation cost of products.
- Higher conductivity: Thermal conductance of dielectic used is 5 to 10 times higher than old epoxy glass.
- More effective and reliable: Thermal transfer is more efficient and reliable than regular PCB.
Aluminum PCB Applications
- Audio device: Input, output amplifier, balanced amplifier, audio amplifier, pre-amplifier,power amplifier.
- Power Supply: Switching regulator, DC / AC converter, SW regulator, etc.
- Communication electronic equipment: High-frequency amplifier, filtering appliances,transmitter circuit
- Office automation equipment: Motor drive, etc.
- Automobile: Electronic regulator, ignition, power supply controller, etc.
- Computer: CPU board, floppy disk drive, power supply devices, etc.
- Power Modules: Inverter, solid state relays, rectifier bridges.
- Lamps and lighting: As the advocated promotion of energy-saving lamps, a variety of colorful energy-saving LED lights are well received by the market, and aluminum pcb used in LED lights also begin large-scale applications.
Types of Aluminum PCB
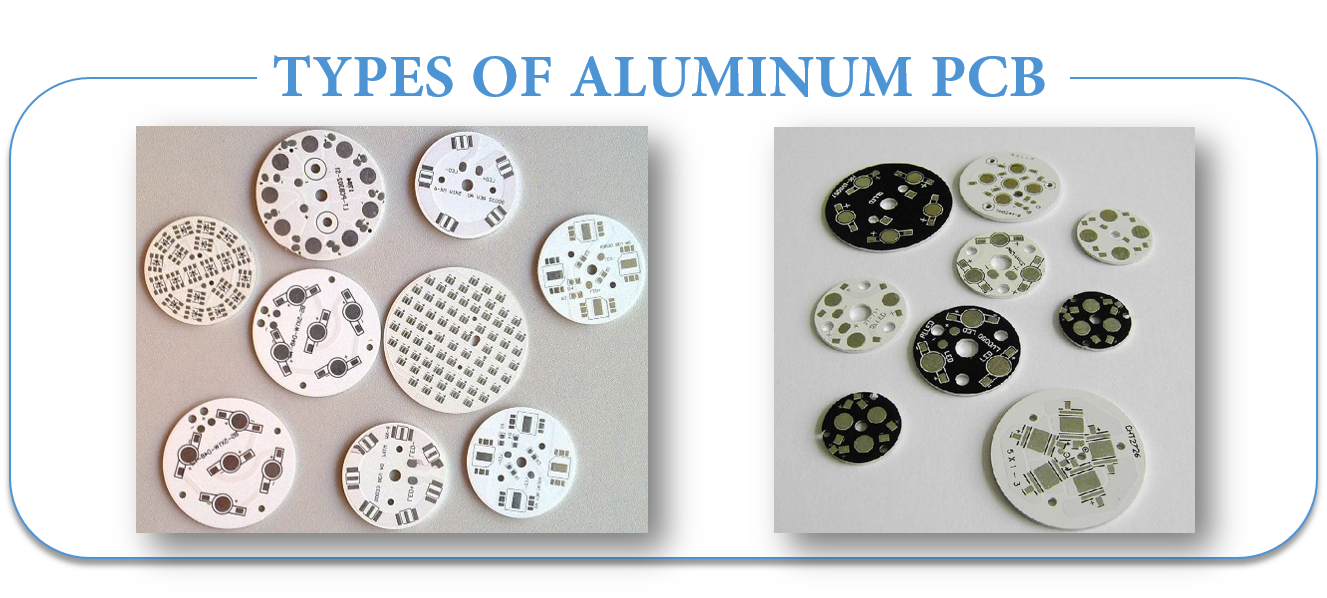
-
Flexible Aluminum PCB
Firstly, Flexible aluminium PCB is a new flexible dielectric developed in the development of aluminium products. It is also a kind of flexible circuit board. Because of the combination of polyimide resin and ceramic filter, it has high flexibility, thermal efficiency and excellent electrical insulation. When used in aluminium PCB products, the expensive cables and connectors no longer need to be used.
Flexible circuit boards have unparalleled flexibility, so flexible aluminum PCB can be arbitrarily folded, twisted or formed in any other desired form. However, it should be noted that once a specific shape is formed, it can no longer be changed like other conventional flexible circuit boards. Or deform.
-
Hybrid Aluminum PCB
In hybrid aluminum construction, non-thermal material is processed and refined separately before it is applied to the thermal materials with aluminum base.
The most common practice is developing 2 layer or 4 layer structure which comprises of FR4 material.
A non thermal material that is bonded with thermal material and aluminum base provides rigidity and helps in the dissipation of heat.
This non thermal bonding is preferred over using all thermal materials because it features less cost and encompasses efficient thermal conductance over regular FR4 products.
No heat sinks or assembly steps are required for the development of this product.
Through hole components can be easily adjusted using component windows on the aluminum base.
This helps in passing the cables and connectors through substrate. Also the seal created by solder fillet eliminates the need of costly adopters.
-
Multilayer Aluminum PCB
Multilayer Aluminum PCBs are very common in power supply products and come with multiple layers of thermally conductive dielectrics.
These materials are very useful when they are combined with one or more layer of circuitry in which thermally conductive dielectric is buried between the layers with the help of blind vias which also act as a signal or thermal vias.
Single layer construction of these designs is not very effective, however, when they come with more complex designs they provide an ideal solution for many applications involving heat dissipation.
-
Through Hole Aluminum PCB
When it comes to most complex constructions, a single layer of aluminum is back-filled and pre-drilled with before applying lamination, forming a Core of a multilayer constructions.
Thermal bonding materials are then used to laminate the thermal materials on both sides of the aluminum.
Once lamination is done, drilling is applied on the assembly.
In order to maintain proper electrical insulation, the plated through holes created as the result of drilling must pass through aluminum clearances.
Aluminum PCB Performance
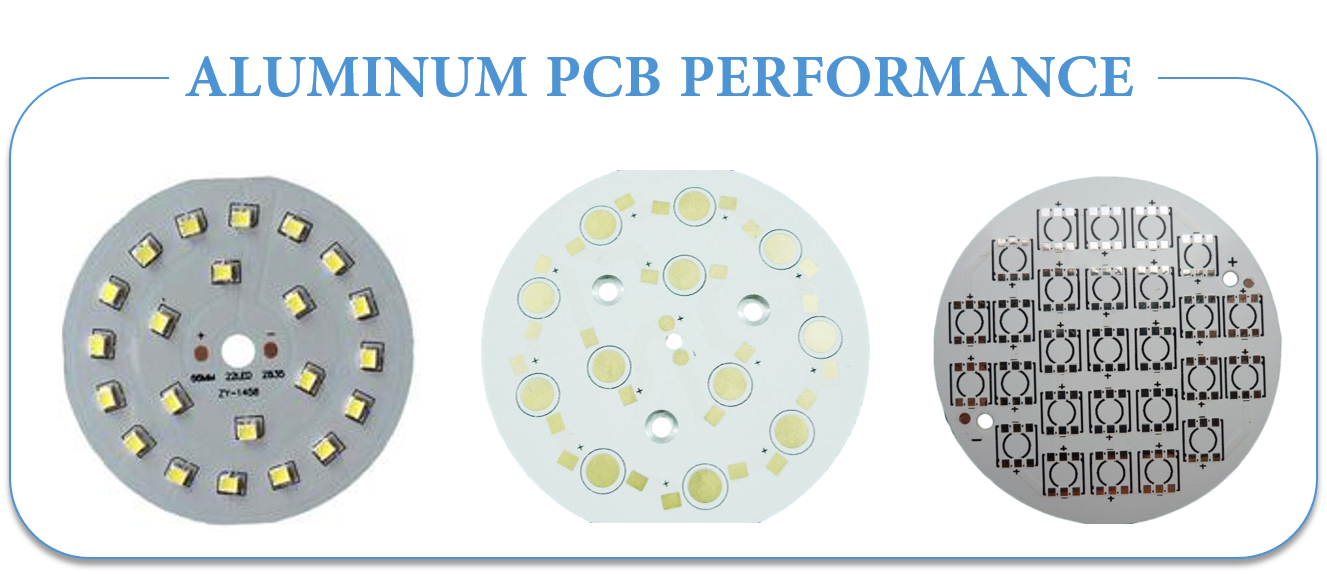
- Better heat dissipation and conductivity: Compared with ordinary FR4 PCB, aluminium PCB has excellent heat dissipation performance. For example, Fr4 PCB with a thickness of 1.5mm will have a thermal resistance of 20-22 degrees per watt, while aluminium PCB with a thickness of 1.5mm will have a thermal resistance of 1-2 degrees per watt.
- There is no serious problem of thermal expansion or contraction.: each substance has its own coefficient of thermal expansion. The CTE of aluminum (22ppm/C) and copper(18ppm/C)is quite close. Since aluminum PCBs work well in terms of Thermal dissipation they do not have severe expansion or contraction issues. They work excellently and are durable and reliable.
- Dimensional Stability: aluminum PCBs show dimensional stability and stable size. For example, when they are heated from 30-140 degrees, their size only had a change by 2.5%-3.0%.
- Others: Aluminum PCBs can be used in power device surface mount technology. They are effective for use in circuit design because of their performance in terms of thermal expansion of circuit design. They help to prolong products shelf life and product power density. They are also extremely reliable. They can help to shrink the overall volume of the product and is also a cheaper option. They show electromagnetic shielding and high dielectric strength.
Classification of Aluminum PCB
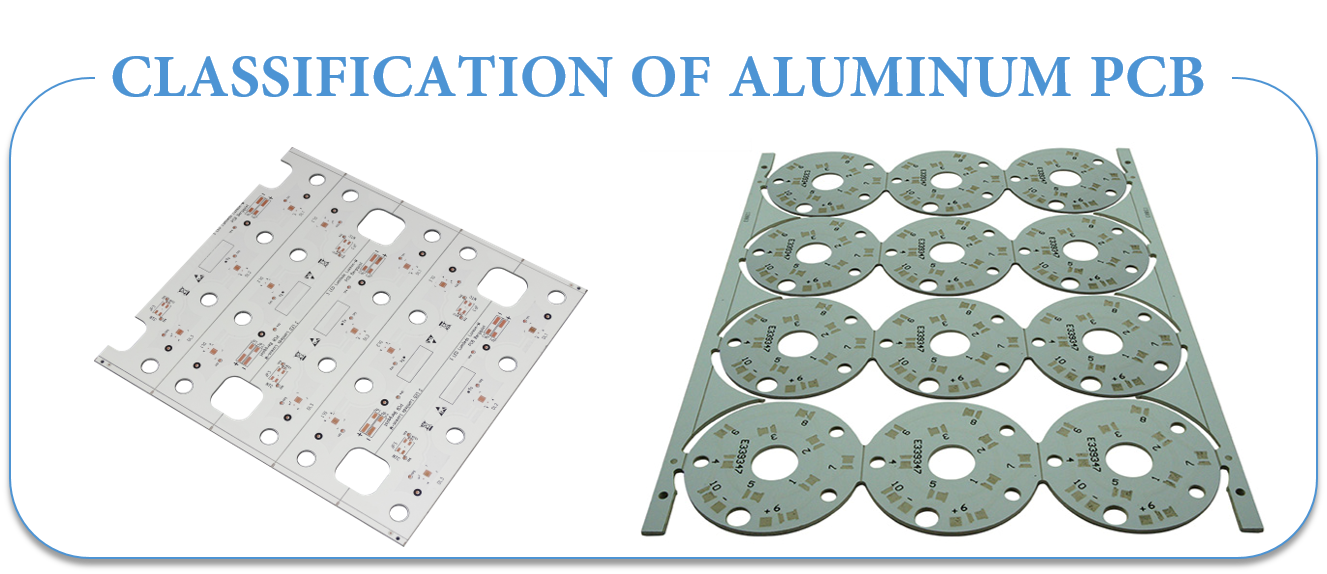
- Universal Aluminum PCB: the dielectric layer used here is made up of epoxy glass fiber pre-preg.
- High Thermal-Conductive Aluminum PCB: the dielectric layer is made up of epoxy resin. The resin used must have high thermal conductivity.
- High-frequency Aluminum PCB: the dielectric layer is composed of polyolefin or polyimide resin glass fiber pre-preg.
Manufacturing Difficulties of Aluminum PCB
The manufacturing process for nearly all aluminum PCBs is essentially the same. Here we will discuss the major manufacturing processes, the difficulties and their solutions.
- Copper Etching: the copper foil used in Aluminum PCBs is comparatively thicker. If the copper foil is over 3oz however, the etching requires width compensation. If it is not according to the demand of the design, the trace width will be out of tolerance after etching. Therefore the trace width compensation should be designed accurately. The etching factors need to be controlled during manufacturing process.
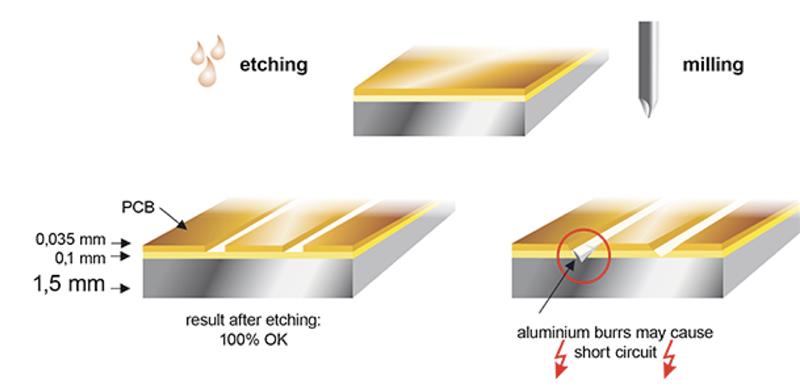
- Solder Mask Printing: due to the thick copper foil there is a difficulty in solder mask printing of aluminum PCB. This is because if the trace copper is too thick then the image etched will have a large difference between trace surface and base board and solder mask printing will be difficult. Therefore, the two-time solder mask printing is used. The solder mask oil used should be of good quality and in some cases the resin filling is done first and then solder mask.
- Mechanical Manufacturing: the mechanical manufacturing process involves mechanical drilling, molding and v-scoring etc. which Is left on internal via. This tends to reduce electrical strength. Therefore, the electric milling and professional milling cutter should be utilized for low-volume manufacturing of products. The drilling parameters should be adjusted to prevent burr from generating. This will help your mechanical manufacturing.
Key Requirements When Selecting an Aluminum PCB Manufacturer
For the most part, all PCB manufacturing follows the same production process regardless of where they are made. The only true differences in suppliers is the level of automation in their process, the newest technology and equipment, and having specific equipment designed to focus on certain types of end products.
For aluminum PCBs, there are several key items that a PCB manufacturer needs to consider if they are going to be able to effectively produce aluminum PCBs in any quantity, including:
- Dedicated Imaging Equipment
Many of our aluminum backed PCBs go into LED applications that are much longer than the standard 18" x 24" or 20" x 24" production panels used in traditional PCB manufacturing. To be able to accurately register and economically produce these parts, a manufacturer must have either a custom piece of 60" wide UV light imaging equipment or a setup capable of screen printing (at one time) an image and then UV curing through an oven.
The old manufacturing process of screen printing half the image and then trying to hand register the first image while screen print the second half is much less effective.
- Specialized Scoring Equipment
The more common equipment that can V score through traditional FR-4 materials is not suited to manage aluminum PCBs. To get the lowest cost possible, we need to get the best yield possible, which means we need to be able to place these parts as close as possible to each other on the production panel. Without V scoring, you must mechanically rout the parts out, which could result in up to 20% loss of your yield, subsequently increasing cost.
Our engineering team has many years of experience helping our customers design arrays that are the most cost effective for them to depanelize.
- Greater Than 40-ton Punch Presses
For aluminum PCBs that are round or have unique features – (slots, large holes, cutouts, etc.) – you will want a manufacturer that can punch out these features. Trying to mechanically rout aluminum PCBs is a very costly way to get these features done in a production environment.
- In-Line Hi-Pot Test
A unique requirement of aluminum PCB is that customers want to know that the product they are getting has passed a hi-pot test. While most PCB manufacturers can do this, it is usually a separate process in a lab that is not located in electrical testing. Epec`s electrical test set up includes a hi-pot test, which dramatically reduces cost for the customer.
The following table presents some of our Aluminum Core materials:
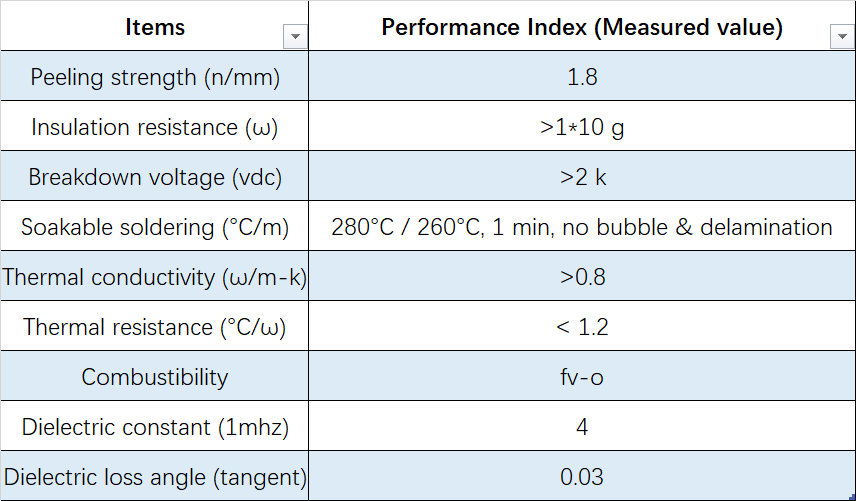
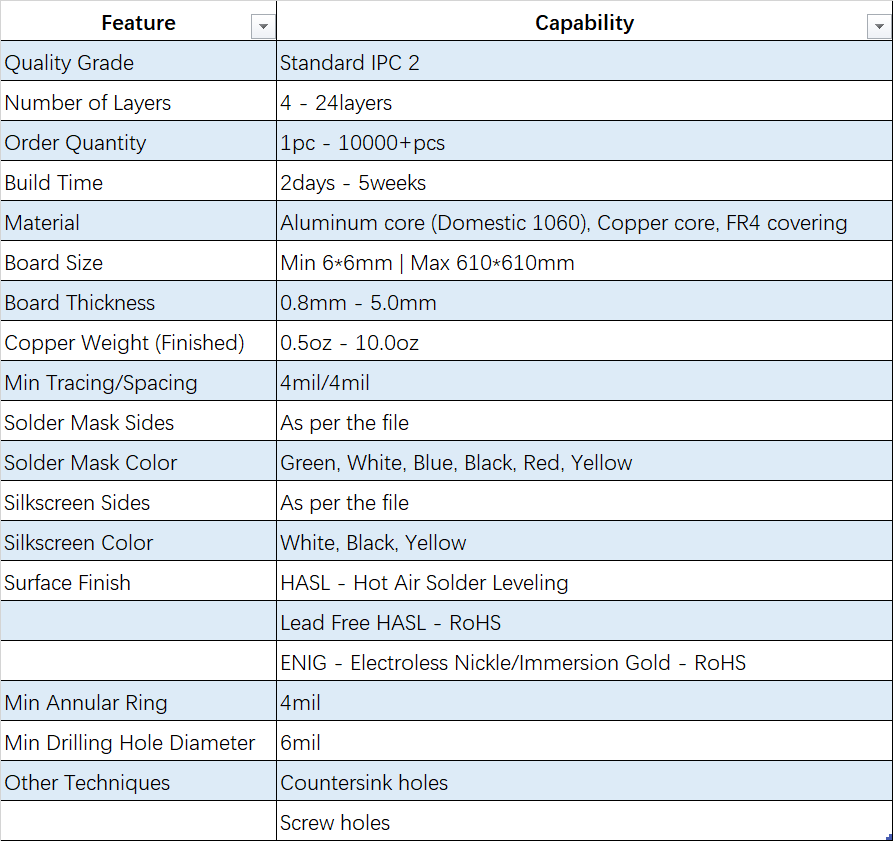
Check our Aluminum core PCB manufacturing capabilities in the following table:
Design Guidelines For Aluminum PCB

The task of aluminum core circuit board is to dissipate the heat generated by power components. Therefore, we recommend installing pure power components in this part of the circuit. The control unit shall be installed on a separate standard PCB.
Drilling distances and diameters
In case of double-sided aluminium-core circuits, the aluminium core must be insulated against throughplating. This is done using an excess of resin when press-moulding the aluminium core with prepregs and copper or by plugging. To this end, the aluminium core must be pre-drilled.
The smallest drilling diameter in the aluminium core is 1,0 mm, the smallest final diameter in the PCB is 0,3 mm. So that the drills are not damaged in these close-set drill holes, a minimum spacing of 1,2 mm is required. This is generally the knock-out criteria for a densely-packed control unit.
Variants of aluminium core circuits
-
Single-sided PCBs on aluminium carriers
Normally, this variant only has drill holes for fastenings.
-
Multilayer PCBs with aluminium core
Copper foils are laminated onto both sides of an aluminium core using prepreg. The PCB can be through-plated. This means that it is also possible to produce multilayers with a 0,5 mm aluminium core.
-
PCBs on metal heat-conducting sheets
Completed PCBs are press-moulded to an aluminium carrier using a prepreg. Benefit: Multilayers can also be used (only single-sided SMD). Partial aluminium carriers are possible. Disadvantage: Poor heat dissipation, as the heat has to be dissipated through the entire PCB.
-
Aluminium-flex
One further possibility is a rigid-flex PCB structure, where the aluminium carrier works as the rigid area of the PCB. This means that it is also possible, for example, to connect a control unit as a plug connector over the exposed flex area.
Basics of Heat Transfer
At a basic level, a discussion about heat transfer includes two topics: temperature and heat flow. Temperature represents the level of thermal energy that`s available, while heat flow represents thermal energy movement from one place to another.
Microscopically, thermal energy is directly related to a molecule`s kinetic energy. The greater the temperature of a material, the greater the thermal agitation of its molecules. It`s normal for areas that contain a lot of kinetic energy to pass it along to areas with less kinetic energy.
There are some material properties that effectively modulate heat that`s transferred between two areas at different temperatures. These include thermal conductivities, material densities, fluid velocities and fluid viscosities. Together, these properties make resolving many heat transfer problems pretty complicated.
The Mechanisms of Heat Transfer
Heat transfer mechanisms can be grouped into three broad categories:
- Conduction. Areas that have more molecular kinetic energy will send their thermal energy to areas that have less molecular energy. This occurs through a direct collision of molecules, known as conduction. In metals, some of the energy transported from one area to another is also carried by conduction-band electrons.
- Convection. When heat is generated in an electronic device, it`s transported via conduction to an are where it is then transferred to a fluid. That process is convection, and the fluid can take the form of a gas such as air or conventional water.
- Radiation. All materials give off thermal energy in amounts that are determined by temperature. When the temperatures are uniform, the radiation flux is in in equilibrium between objects, and there is no exchange of thermal energy. This balance changes when temperatures vary and thermal energy is transported from areas of higher temperatures to those of lower temperature.
HELP RESOURCES
Quick Turn Aluminum PCB
Aluminium PCB Board for LED
Aluminium Base Metal Core PCB
Aluminum PCBs vs. Standard PCBs
Using aluminium in flexible Circuits Board
Things You Need To Know About Aluminum PCBs
Aluminum PCB,Aluminum PCB Led,Aluminum Core PCB,Aluminum Circuit Board
JingHongYi PCB (HK) Co., Limited , https://www.pcbjhy.com